

The terms ‘investing’ and ‘trading’ are often used interchangeably. However, there are key differences between the two financial strategies. The goal of investing is generally to build wealth over the medium to long term. By contrast, the goal of trading is to generate profits in the short-term. In this guide, we take a look at the basics of investing and trading and explain how the two financial strategies differ.
Investing is a longer-term ‘buy-and-hold’ strategy. Investors will often hold assets for years, or even decades, with the aim of generating substantial profits from rising asset prices and any income generated from the assets over time.
An investor’s exact time horizon (the length of time that the investor expects to invest for) will depend on their financial objectives. For example, someone who is investing for retirement may have a time horizon of 20 years or longer. Someone who is investing to build up a house deposit, on the other hand, may have a time horizon of five years.
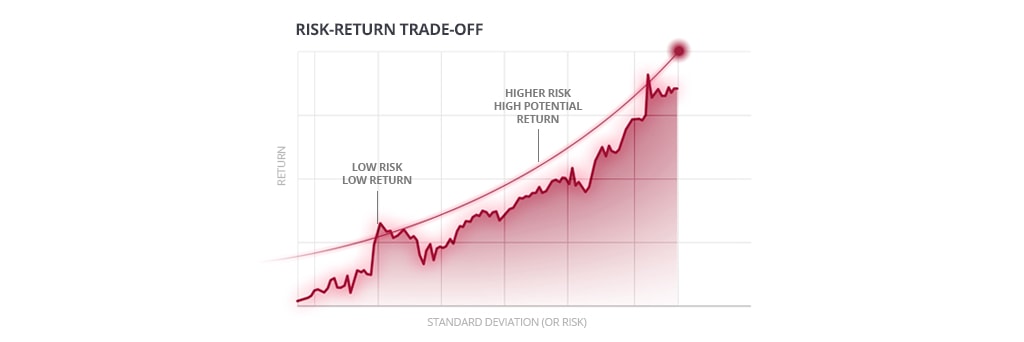
A fundamental principle of investing is that the higher the potential return of an investment, the higher the risk of that investment. This is known as the ‘risk-return tradeoff.’ Risk refers to the chance that an investment’s actual returns will differ from its expected returns.
The longer an investor’s time horizon, the more they can focus on higher-growth, higher risk investments. This is because they have more time to ride out market volatility. An investor with a shorter time horizon will need to be more conservative with their investment choices otherwise they run the risk of not achieving their financial goals.
Most investors are comfortable with the fact that financial markets tend to rise and fall in the short term. As a result, they will often ride out periods of underperformance with the expectation that asset prices will eventually rebound and any short-term losses will be recovered.
There are two main styles of investing. These are:
Active investing: in this approach, investors actively buy and sell securities for their portfolio with the aim of outperforming an investment benchmark index over time. An active stock market investor, for example, might buy 30 individual stocks with the aim of outperforming the S&P 500 index (a stock market index that is composed of 500 large US companies).
Passive investing: the goal of passive investing is simply to match the performance of a market or benchmark index over time. In this approach, investors do not pick individual securities for their portfolio. Instead, they invest in benchmark-based funds, such as exchange-traded funds (ETFs) and index funds, that aim to track the performance of a market.
Compared to investing, trading is a more active, short-term-focused strategy.
Traders tend to hold assets for a much shorter period of time than investors, often buying and selling securities within weeks, days, or even hours, with the aim of profiting from short-term price movements.
Whereas investors mainly seek to profit from rising asset prices, traders look to profit from both rising and falling asset prices. Instead of focusing on an asset’s long-term growth prospects like investors do, traders focus on which direction the asset’s price is likely to head in next and try to profit from that price movement.
While investors often ride out periods of underperformance, traders are more likely to use ‘stop-loss’ orders to automatically close out losing trades at a predetermined price level. This helps to protect trading capital.
Compared to investing, trading generally requires more time commitment. Whereas an investor can buy a stock or fund and forget about it, a trader needs to be constantly monitoring market developments.
There are a number of different trading styles that traders pursue. These include:
Scalping: this is a trading strategy that aims to capture small profits, repeatedly. It involves holding a position for a very short amount of time – perhaps just a few minutes or even less.
Day trading: this approach to trading involves opening and closing positions within a single day. Closing a trade before the market closes reduces the risks of receiving unfavorable news overnight.
Position trading: the goal of position trading is to profit from dominant price trends. A trend occurs when an asset’s price moves in one direction for an extended period of time.
Swing trading: the aim of swing trading is to focus on larger price movements, rather than identifying the start and finish of a price trend. In this strategy, positions may be held for days to weeks.
Aside from the fact that investing is more long-term focused while trading is more short-term focused, there are plenty of other differences between the two strategies.Here’s a look at three key differences between investing and trading.
The main asset class that investors focus on is stocks.
Stocks, or ‘shares’ as they are often called, are investments that represent ownership in a company.
Investing in stocks can be a great way to grow your wealth over time. Historically, stocks have delivered excellent returns to investors over the long term.
For example, since the inception of the S&P 500 index in 1926, it has risen by around 10% per year on average.
This is a much higher return than the returns generated by other assets such as bonds and cash savings.
Some investors like to pick individual stocks (such as Apple, Amazon, and Microsoft) themselves. Others prefer to invest in stocks through funds and ETFs that provide broad exposure to the stock market.
Investors also often add other assets to their portfolios in an effort to enhance their returns and lower their portfolio risk. For example, an investor might own a selection of stocks and ETFs, as well as some commodities such as gold and silver, and some cryptoassets such as Bitcoin and Ethereum.
Compared to investors, traders focus on a wider range of asset classes. For example, there are traders that focus on stocks, indices, currencies, commodities, and cryptoassets.
Generally speaking, traders tend to prefer more volatile asset classes as it’s volatility that creates trading opportunities.
The main asset class that investors focus on is stocks.
Stocks, or ‘shares’ as they are often called, are investments that represent ownership in a company.
Investing in stocks can be a great way to grow your wealth over time. Historically, stocks have delivered excellent returns to investors over the long term.
For example, since the inception of the S&P 500 index in 1926, it has risen by around 10% per year on average.
This is a much higher return than the returns generated by other assets such as bonds and cash savings.

Some investors like to pick individual stocks (such as Apple, Amazon, and Microsoft) themselves. Others prefer to invest in stocks through funds and ETFs that provide broad exposure to the stock market.
Investors also often add other assets to their portfolios in an effort to enhance their returns and lower their portfolio risk. For example, an investor might own a selection of stocks and ETFs, as well as some commodities such as gold and silver, and some cryptoassets such as Bitcoin and Ethereum.
Compared to investors, traders focus on a wider range of asset classes. For example, there are traders that focus on stocks, indices, currencies, commodities, and cryptoassets.
Generally speaking, traders tend to prefer more volatile asset classes as it’s volatility that creates trading opportunities.